The Society of Actuaries (SOA) is a professional organization that provides education and certification for actuaries. Actuaries are professionals who use mathematical and statistical methods to assess risk in industries such as insurance and finance. One of the exams offered by SOA is the FM Exam, which focuses on financial mathematics and is a requirement for becoming a certified actuary.
Once a candidate takes the FM Exam, they eagerly await the results to determine if they have passed and are one step closer to their goal of becoming a certified actuary. The SOA releases the exam results several weeks after the exam date, and candidates anxiously check their emails or log into the SOA’s website to see their results.
Receiving the FM Exam results can be a nerve-wracking experience for candidates. Passing the exam is a significant accomplishment and signifies the candidate’s understanding of financial mathematics concepts and their ability to apply them in real-world scenarios. On the other hand, failing the exam can be discouraging, but it is not the end of the road. Candidates can retake the exam and use their score report to identify areas of weakness and focus their study efforts.
In this article, we will explore the process of receiving SOA FM Exam results, the impact of passing or failing the exam, and the resources available to candidates for exam preparation and study. We will also discuss the importance of the FM Exam in becoming a certified actuary and the opportunities that await successful candidates in the actuarial profession.
What is the SOA FM Exam?
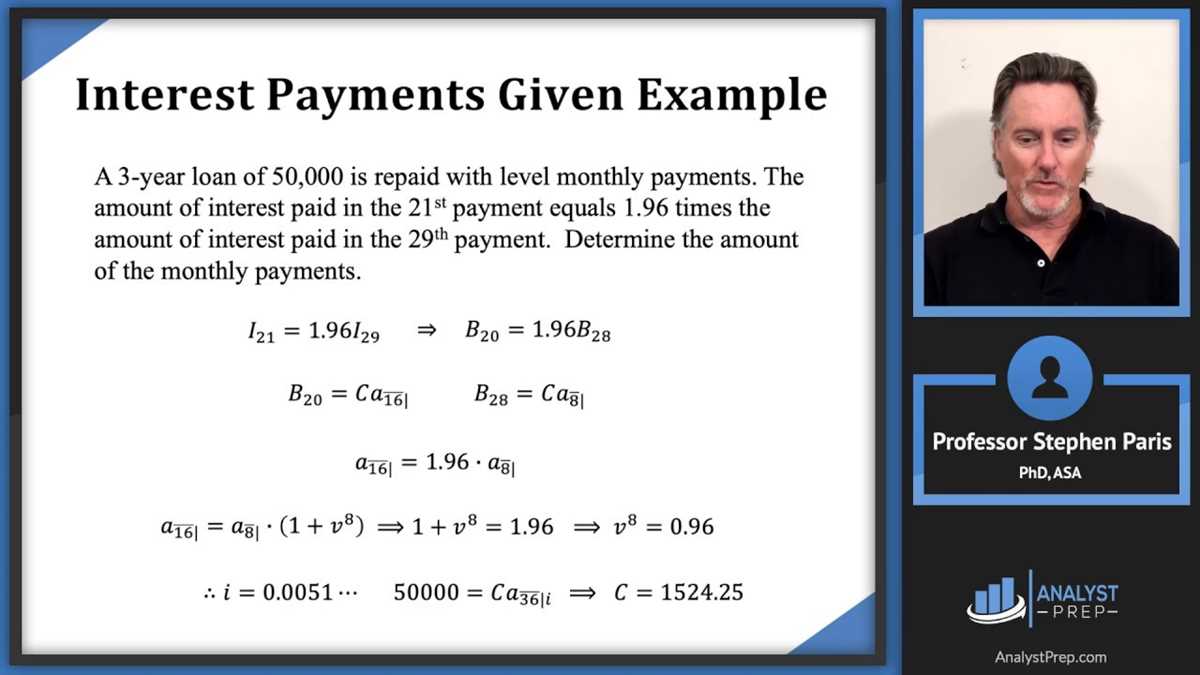
The SOA FM Exam, also known as the Financial Mathematics Exam, is a professional examination administered by the Society of Actuaries (SOA) in the field of actuarial science. It is designed to assess candidates’ understanding and proficiency in financial mathematics concepts and their application in various financial scenarios.
This exam covers a wide range of topics, including interest theory, derivative instruments, risk management, investment analysis, and portfolio management. It requires candidates to have a strong foundation in mathematics, including calculus and probability theory, as well as a solid understanding of financial concepts and models.
Successful completion of the SOA FM Exam is an important step for individuals looking to become certified actuaries. The exam is typically taken by students or professionals in the actuarial field who are seeking to enhance their knowledge and skills in financial mathematics. Passing this exam demonstrates a strong understanding of the principles and practices used in financial modeling and risk management, making candidates more competitive in the actuarial job market.
The Importance of the SOA FM Exam Results
In the field of actuarial science, the SOA FM exam is a crucial milestone for aspiring actuaries. The exam assesses the candidates’ understanding of the financial mathematics concepts and principles that are fundamental to the actuarial profession. The results of this exam are of utmost importance for several reasons.
1. Career Advancement: The SOA FM exam is one of the early exams that actuaries must pass to progress in their careers. Obtaining good results in this exam demonstrates a strong foundation in financial mathematics, which is essential for actuaries in various job roles, such as investment analysis, risk management, and insurance product pricing. Employers often consider the FM exam results when making hiring decisions and promotions.
2. Professional Competence: Actuaries play a crucial role in financial institutions and insurance companies, where they make significant decisions based on complex financial models. The FM exam tests candidates on their ability to apply mathematical concepts and principles to solve real-life problems. Successful performance in this exam ensures that the actuaries have the necessary competence to provide accurate and reliable financial analysis and projections.
3. Continued Learning: Actuarial science is a constantly evolving field, and actuaries are required to continuously update their knowledge and skills. The FM exam results give candidates valuable feedback on their understanding of financial mathematics concepts. This feedback helps them identify their strengths and weaknesses, allowing them to focus their efforts on areas that require improvement. Actuaries who consistently perform well in their exams show a dedication to ongoing education and professional development.
In conclusion, the SOA FM exam results hold great significance in the actuarial profession. They serve as a benchmark for career advancement, demonstrate professional competence, and facilitate continued learning and improvement. Actuaries who obtain good results in the FM exam are more likely to succeed in their careers and make meaningful contributions to the field of actuarial science.
Understanding the SOA FM Exam
The SOA FM exam, or Financial Mathematics exam, is one of the exams offered by the Society of Actuaries (SOA) to qualify individuals for certification as an actuary. This exam focuses on the application of financial mathematics concepts and techniques in the context of insurance and other financial services. It is an essential step towards becoming a qualified actuary.
The exam covers a broad range of topics, including interest rates, annuities, loans, bonds, portfolios, options, and risk management. It requires a solid understanding of mathematical concepts and formulas, as well as the ability to apply them to real-world scenarios. Candidates are expected to have a strong foundation in calculus, probability, and statistics.
To prepare for the exam, candidates are advised to study various textbooks and online resources that cover the required topics. It is also recommended to practice solving sample problems and past exam questions to become familiar with the exam format and style of questions. Additionally, attending review courses or joining study groups can be helpful in gaining a deeper understanding of the material and clarifying any uncertainties.
The exam itself consists of multiple-choice questions and has a time limit of four and a half hours. It is administered in a computer-based format and can be taken at designated testing centers. After completing the exam, candidates will receive their results within a few weeks. Passing the FM exam is an important milestone on the path to becoming an actuary and demonstrates proficiency in financial mathematics concepts and techniques.
Exam Format and Structure

The SOA FM exam consists of multiple-choice questions and is administered via computer-based testing. The exam is divided into two sections, with a total of 35 questions in each section, for a total of 70 questions. Each question has five possible answer choices, of which only one is correct.
The exam covers a wide range of topics related to financial mathematics, including interest rates, time value of money, discounting, annuities, and various mathematical techniques used in finance. The questions are designed to test candidates’ knowledge and understanding of these topics, as well as their ability to apply the concepts to solve real-world problems.
Candidates are provided with a four-function calculator and a formula sheet during the exam. The use of any other calculators or external materials is strictly prohibited. The exam duration is 3 hours and 15 minutes, with an additional 30 minutes for a tutorial and introductory screens.
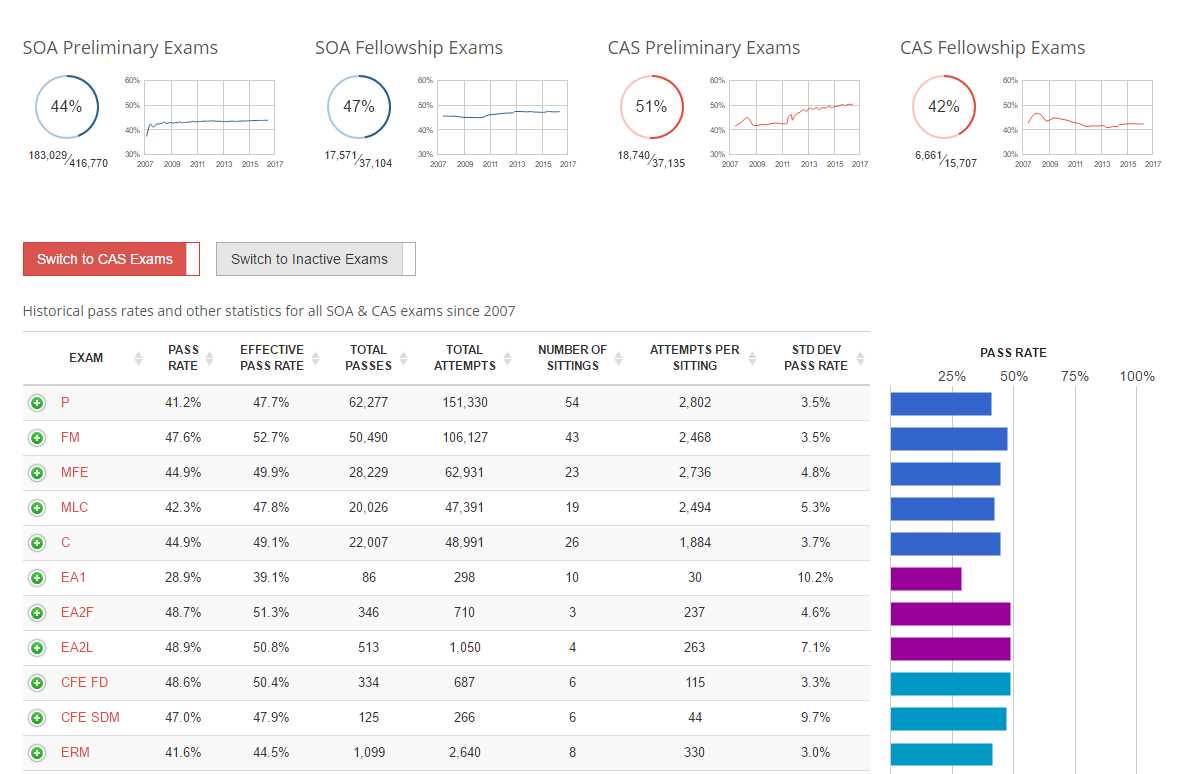
Upon completion of the exam, candidates will receive their preliminary score report immediately. The official exam results will be available within 8 weeks of the exam date. A passing score is determined by the SOA, and the results are reported as a scaled score between 0 and 10, with 6 being the minimum passing score.
Key Topics Covered in the Exam

The SOA FM exam covers a wide range of topics related to financial mathematics and financial economics. Some of the key topics that are included in the exam syllabus are:
- Time value of money: This topic covers concepts such as present value, future value, annuities, and perpetuities. Candidates need to demonstrate their understanding of the principles and formulas used to calculate these values.
- Interest theory: This section focuses on the different interest rates and their applications in various financial scenarios. Candidates should be able to analyze and solve problems related to simple and compound interest.
- Discounted cash flow applications: This topic involves understanding the concept of discounted cash flow and its applications in capital budgeting, investment decisions, and valuation of financial assets.
- Bond valuation: Candidates are expected to have a good grasp of bond pricing, yield measures, duration, and convexity. They should be able to calculate the value of a bond using different methods and interpret the results.
- Asset pricing models: This section introduces various asset pricing models, such as the capital asset pricing model (CAPM) and the arbitrage pricing theory (APT). Candidates need to understand the assumptions, limitations, and implications of these models.
- Options and derivatives: Candidates should have a solid understanding of options, futures, and other derivative instruments. They should be able to calculate option prices, understand option strategies, and analyze the impact of different factors on option values.
These topics are designed to test candidates’ knowledge and ability to apply financial mathematics concepts in real-world scenarios. It is important for candidates to familiarize themselves with these topics and practice solving problems related to each area to prepare effectively for the SOA FM exam.
How are SOA FM Exam Results Calculated?
Calculating the results for the Society of Actuaries (SOA) Financial Mathematics (FM) exam is a meticulous process that involves several steps. The exam is designed to assess candidates’ understanding and application of mathematical concepts in the field of actuarial science.
To determine the results, the SOA uses a combination of raw scores and a scaling process. Each question in the exam is assigned a certain number of points, and candidates earn points based on their correct answers. The raw score is then calculated by summing up the points earned for each correct answer.
After the raw scores are determined, the next step is to apply a scaling process to ensure that the exam results are fair and comparable across different test administrations. The scaling process takes into account the difficulty level of the exam and adjusts the scores accordingly. This helps to account for any variations in the difficulty level between different administrations of the exam.
Once the scaling process is completed, the final scaled score is calculated. This scaled score is what actuaries use to determine whether a candidate has passed the exam. The passing score for the FM exam is determined by the SOA based on statistical analysis and is subject to periodic review and adjustment.
In summary, the SOA FM exam results are calculated using a combination of raw scores and a scaling process to ensure fairness and comparability. This rigorous process helps to determine the knowledge and understanding of candidates in the field of financial mathematics and actuarial science.
Grading Criteria for the Exam
Earning a good score on the Soa fm exam requires a thorough understanding of the grading criteria. The exam is divided into different sections, each assessing specific competencies in the field of financial mathematics. Here are the key aspects that are taken into account when evaluating your performance:
- Conceptual Knowledge: You will be assessed on your understanding of the fundamental concepts and theories related to financial mathematics. This includes topics such as interest rates, annuities, and time value of money.
- Problem Solving: The ability to effectively apply your mathematical skills and knowledge to solve complex problems is a crucial component of the exam. You will be evaluated on your problem-solving strategies, accuracy, and efficiency.
- Logical Reasoning: Logical reasoning skills are essential for analyzing and interpreting financial data and scenarios. Your ability to identify patterns, make connections, and draw logical conclusions will be assessed.
- Communication: Effective communication is vital in the field of financial mathematics. You will be evaluated on your ability to clearly articulate your mathematical reasoning and solutions, both in written and verbal formats.
- Time Management: The exam is time-limited, so efficient time management is crucial. You will be assessed on your ability to allocate your time wisely and complete the exam within the given timeframe.
It’s important to keep these grading criteria in mind as you prepare for the Soa fm exam. By focusing on developing a strong conceptual knowledge, practicing problem-solving techniques, honing your logical reasoning skills, improving your communication abilities, and mastering time management, you can maximize your chances of achieving a high score.
Explanation of Pass, Credit, and Fail classifications
When the results of the SOA FM exam are released, candidates are classified into three categories: Pass, Credit, and Fail. These classifications are determined based on the candidate’s performance on the exam.
Pass: Candidates who receive a Pass classification have demonstrated a strong understanding of the concepts covered in the exam. They have successfully answered a significant portion of the questions correctly and have met the minimum requirements set by the examiners. A Pass classification indicates that the candidate has a solid foundation of knowledge in the subject area.
Credit: Candidates who receive a Credit classification have performed well on the exam, but have not met all the criteria for a Pass. They have demonstrated a good understanding of the concepts and have correctly answered a sufficient number of questions. While they may have missed some of the more difficult or complex questions, their performance is still commendable and indicates a solid understanding of the subject matter.
Fail: Candidates who receive a Fail classification have not met the minimum requirements set for the exam. They have either answered a small number of questions correctly or have not demonstrated a sufficient understanding of the concepts. A Fail classification indicates that the candidate needs to further review and study the material before attempting the exam again.