
Understanding the complexities of human geography is essential for comprehending the interconnectedness of our world. In AP Human Geography Chapter 3, we delve into the study of cultural patterns and processes, exploring the various factors that shape societies and their interactions. This study guide provides comprehensive answers to key questions, offering insights into the diverse range of human behaviors, beliefs, and practices.
As we explore the chapter, we encounter a broad range of questions. How do cultures diffuse and change? What factors contribute to the spatial distribution of languages, religions, and ethnicity? By answering these questions, we gain a deeper understanding of how cultural landscapes are shaped and how patterns of cultural diversity emerge. This study guide offers detailed explanations and analysis to help you unravel the intricacies of these processes.
In this chapter, we also delve into the significance of language and religion in shaping cultural landscapes. How do languages evolve and influence cultural identities? What role does religion play in shaping societies and their connections? By examining these questions, we uncover the influential role that languages and religions play in establishing cultural boundaries and fostering social cohesion.
With the help of this study guide, you will uncover the answers to these questions and more, expanding your knowledge of human geography and the complex web of factors that determine the distribution of cultures and their patterns. By unlocking these patterns, you will gain a greater appreciation for the diversity of the world we live in and the cultural interactions that shape our lives.
AP Human Geography Chapter 3 Study Guide Answers
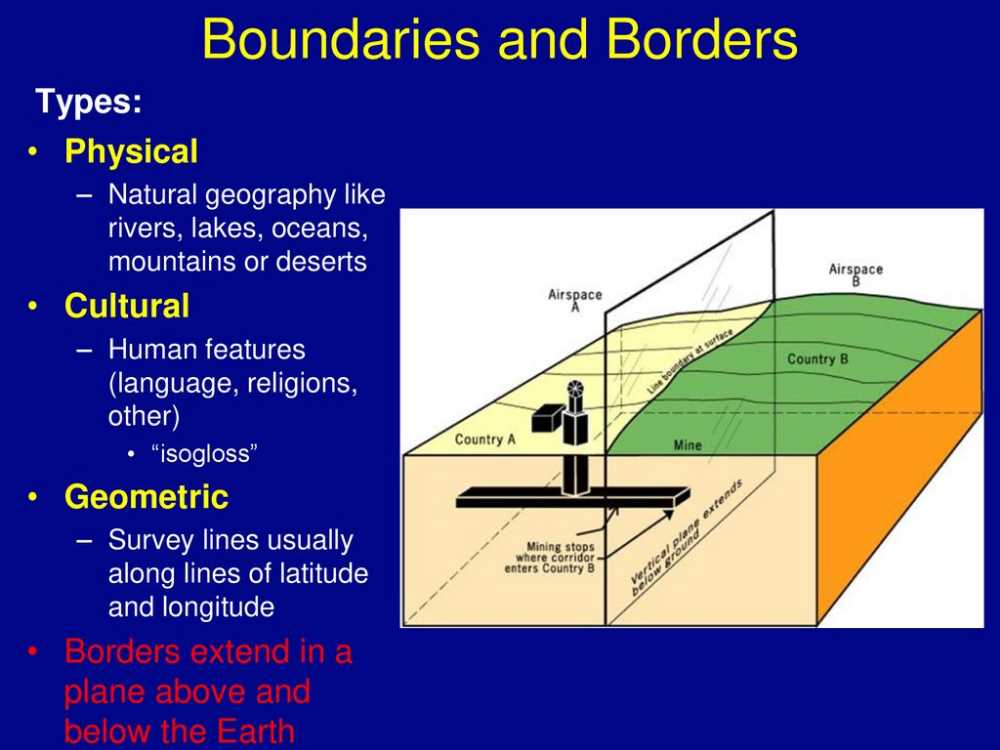
In this study guide, we will explore the answers to some key questions from Chapter 3 of AP Human Geography. This chapter focuses on the topic of population, specifically discussing concepts such as population density, population distribution, population growth, and migration.
1. What is population density?
Population density refers to the number of individuals within a specific area, typically measured in terms of square miles or square kilometers. It is calculated by dividing the total population of an area by its land area. Population density can vary significantly from one region to another, with some areas being densely populated and others sparsely populated.
2. What factors influence population distribution?
Several factors influence population distribution, including physical geography, climate, availability of resources, and economic opportunities. Physical geography features such as mountains, rivers, and coastlines can impact where people choose to live. Climate conditions also play a role, with people often preferring areas with mild temperatures and ample rainfall. Additionally, regions with abundant natural resources or strong economic prospects tend to attract more population.
3. What are the different types of population growth?
There are three main types of population growth: exponential growth, linear growth, and negative growth. Exponential growth occurs when a population increases at an accelerating rate, often due to high birth rates and limited resources. Linear growth refers to a steady increase in population over time, while negative growth occurs when the population declines due to factors such as low birth rates and emigration.
4. What are the push and pull factors in migration?
Migration is the movement of individuals from one place to another. Push factors are factors that compel people to leave their current location, such as lack of economic opportunities, political instability, or environmental disasters. Pull factors, on the other hand, are factors that attract people to a particular destination, such as better job prospects, political stability, or a higher quality of life.
5. How does population mobility impact regions?
Population mobility, which refers to the movement of people within or between regions, can have significant impacts on both the origin and destination regions. In the origin region, population outflows can lead to a decrease in population and a loss of human resources. Conversely, in the destination region, population inflows can bring about demographic changes, economic growth, and cultural shifts.
In conclusion, Chapter 3 of AP Human Geography delves into the topic of population and explores various aspects related to population density, distribution, growth, and migration. Understanding these concepts is crucial for analyzing and interpreting patterns of human settlement and movement across the globe.
What is AP Human Geography?
AP Human Geography is a high school course that examines the human population from a geographic perspective. It explores the patterns and processes that shape human societies, including how people interact with their environment, how they organize themselves into communities, and how they create and maintain cultural landscapes.
This course focuses on key concepts such as population and migration, cultural patterns and processes, political organization of space, agricultural and rural land use, and urbanization. It also aims to develop students’ understanding of the spatial connections between human populations and the natural world, as well as the interrelationships between different regions.
Students in AP Human Geography analyze geographic data, study maps and graphs, and use spatial concepts to understand the complexities of human society. They learn to think critically, draw connections between concepts, and develop a global perspective. This course prepares students to take the AP Human Geography exam, which can provide college credit and demonstrate proficiency in the subject.
Why is Chapter 3 important?

In the study of AP Human Geography, Chapter 3 holds significant importance as it explores the concept of population. Understanding population dynamics is crucial for analyzing social, economic, and political patterns and their impact on the environment. This chapter provides the foundation for comprehending the distribution, growth, and movement of human populations around the world.
Population distribution: Chapter 3 delves into the various factors and processes that shape population distribution. It discusses the significance of physical and human factors such as climate, topography, resources, and cultural preferences in determining where people choose to live and settle. Understanding population distribution helps geographers analyze patterns of urbanization, access to resources, and the development of infrastructure.
Population growth and decline: Another key aspect covered in Chapter 3 is population growth and decline. This chapter explores demographic indicators such as birth rates, death rates, fertility rates, and migration patterns that affect population change. Examining these factors allows geographers to understand the challenges and consequences associated with population growth, including strain on resources, social and economic implications, and the need for sustainable development.
Migration: Chapter 3 also focuses on migration, a significant component of human population dynamics. Geographers study the reasons, push-pull factors, and patterns of migration to better comprehend the impacts on both the origin and destination regions. Understanding migration is essential for analyzing the cultural, social, and economic implications it brings, as well as the changes it may cause in communities.
In conclusion, Chapter 3 plays a crucial role in AP Human Geography as it provides a comprehensive understanding of population dynamics. It allows geographers to analyze population distribution, growth, and migration patterns, which are essential for studying human-environment interactions and making informed decisions regarding sustainable development and resource management.
Key Concepts to Understand in Chapter 3
In Chapter 3 of the AP Human Geography course, students will delve into key concepts related to population and migration. It is important to understand these concepts as they provide crucial insights into the patterns, processes, and impacts of population growth and movement.
One of the key concepts in this chapter is population distribution, which refers to the spatial pattern of where people live. Factors like physical geography, climate, resources, and economic opportunities influence population distribution. Understanding population distribution helps us analyze and predict population trends within certain regions.
Population growth and its determinants
- Natural increase: the difference between birth rates and death rates, which can lead to population growth or decline.
- Fertility: the average number of children born to women in a given population. Factors such as social and cultural norms, access to healthcare, and economic opportunities influence fertility rates.
- Mortality: the death rate within a population. Factors such as healthcare infrastructure, nutrition, and disease prevalence impact mortality rates.
- Migration: the movement of people from one place to another. It can be voluntary or forced and is influenced by factors such as economic opportunities, political instability, and environmental conditions.
Population composition and its impacts

- Age structure: the distribution of individuals in different age groups within a population. Understanding age structure helps determine the potential for population growth or decline and impacts social, economic, and political dynamics.
- Dependency ratio: the ratio between the economically dependent population (those too young or old to work) and the working-age population. This ratio affects economic productivity and social support systems.
- Gender: the social and cultural roles, expectations, and differences between males and females within a population. Understanding gender dynamics is crucial for studying social and economic inequality, as well as addressing gender-related issues.
- Ethnicity and race: the cultural and genetic characteristics that differentiate people within a population. Ethnicity and race play a significant role in shaping identity, social integration, and political dynamics.
What are the answers to the study guide questions?
Below are the answers to the study guide questions for the AP Human Geography Chapter 3.
Question 1: What are the three major types of migration?
- Voluntary migration: People choose to move to a new location for better opportunities, such as economic, social, or political reasons.
- Involuntary migration: People are forced to move due to factors beyond their control, such as conflict, natural disasters, or government policies.
- Internal migration: People move within the same country, often from rural to urban areas, in search of better living conditions or job opportunities.
Question 2: What are the four conditions necessary for a migration transition?
- Improved economic conditions: People need economic opportunities and resources to be able to afford to migrate.
- Technological advancements: Transportation and communication technologies need to be accessible and affordable for people to migrate.
- Changes in social and cultural factors: Attitudes towards migration, family structure, and social networks can influence migration patterns.
- Political factors: Government policies, such as immigration laws and border control, can either encourage or restrict migration.
Question 3: What are the different theories of migration?
- Push-pull theory: This theory states that people are pushed out of their home countries due to negative factors (push factors) and pulled towards destination countries due to positive factors (pull factors).
- Intervening obstacle theory: This theory suggests that factors like distance, cost, and bureaucracy can act as barriers that inhibit migration.
- Gravity model: This model states that migration flows are influenced by the size of population and distance between places, with larger populations and shorter distances resulting in greater migration flows.
Question 4: What are the different types of refugee movements?
- Refugees: People who are forced to flee their home countries due to well-founded fear of persecution, conflict, or violence.
- Internally displaced persons (IDPs): People who have been forced to leave their homes but have not crossed an international border.
- Asylum seekers: Individuals who have left their home countries and are seeking protection in another country.
Question 5: What are the impacts of migration on both the sending and receiving countries?
- Sending countries may experience loss of skilled labor, brain drain, and decreased population, which can impact their economic development.
- Receiving countries may benefit from an increase in labor force, cultural diversity, and economic growth, but may also face challenges related to social integration, strain on resources, and competition for jobs.
These are the answers to the study guide questions for Chapter 3 of AP Human Geography. By understanding these concepts, you will have a better understanding of patterns and impacts of migration in different regions of the world.
How to Memorize the Answers for Chapter 3?
Memorizing the answers for Chapter 3 of AP Human Geography can be a challenging task, especially when dealing with a lot of information and concepts. However, with the right approach and techniques, you can master the material and recall the answers effectively. Here are some tips to help you memorize the answers:
1. Understand the concepts:
Before memorizing the answers, it is crucial to have a solid understanding of the concepts presented. Take the time to read and comprehend the chapters, paying attention to the key ideas and examples provided. This will provide a foundation for memorizing the answers more efficiently.
2. Create visual aids:
Visual aids can be powerful tools for memorization. Use diagrams, flow charts, or concept maps to visualize the relationships between different topics and subtopics. Color coding or using symbols can also aid in retaining the information.
3. Use mnemonic devices:
Mnemonic devices are memory techniques that help you remember information more easily. Create acronyms, rhymes, or associations that connect the answers to familiar words or phrases. For example, you can create a phrase using the first letter of each answer or associate specific answers with memorable images.
4. Practice active recall:
Instead of simply re-reading the answers, actively recall the information from memory. Testing yourself through flashcards, practice quizzes, or verbal recitation can strengthen your memory retrieval and identify areas that need further review.
5. Break it down:

Don’t try to memorize everything at once. Break the answers into smaller, manageable chunks and focus on one section at a time. This approach allows for better retention and prevents overwhelming yourself with too much information.
6. Review regularly:
Regularly reviewing the answers is essential for long-term retention. Set aside dedicated study time each day or week to go over the material. Spacing out your review sessions over time will reinforce your memory and prevent forgetting.
By incorporating these techniques into your study routine, you can improve your ability to memorize the answers for Chapter 3 of AP Human Geography. Remember to stay consistent, be patient with yourself, and make adjustments as needed. Good luck!