Geometry is an essential subject for seventh graders to grasp as it lays the foundation for more advanced mathematical concepts. Understanding geometric shapes, angles, and measurements is crucial not only for academic success but also for everyday life. In this article, we will explore seven common geometry questions that seventh graders often encounter and provide detailed answers to help them enhance their knowledge of this fascinating field.
One of the fundamental concepts in geometry is understanding the properties and characteristics of different shapes. Students may often encounter questions asking them to identify the attributes of various polygons such as triangles, quadrilaterals, and pentagons. By learning about the number of edges, vertices, and angles of these shapes, seventh graders can develop a solid understanding of their geometrical properties.
Another important area of geometry that seventh graders typically delve into is measurement. Questions may arise regarding how to calculate the area and perimeter of different shapes, such as rectangles, squares, and circles. Mastering the formulas for these calculations allows students not only to solve mathematical problems but also to apply their knowledge to real-world situations, such as measuring the dimensions of a room or determining the amount of material needed for a project.
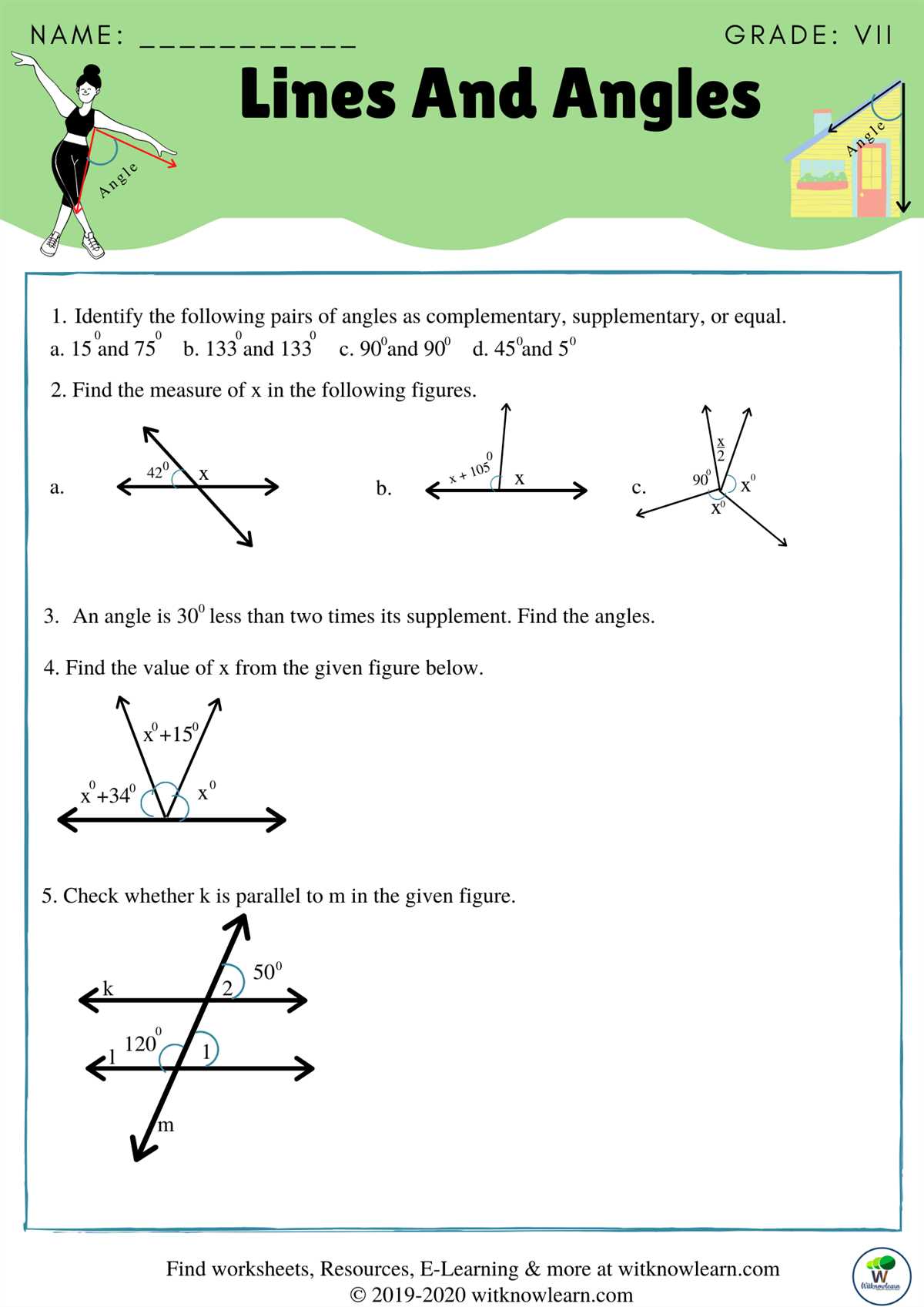
Furthermore, angles play a significant role in geometry, and students are often presented with questions involving the measurement and classification of angles. Understanding the various types of angles, including acute, obtuse, and right angles, helps students analyze shapes and solve equations involving angles. Additionally, learning about complementary and supplementary angles enables students to identify relationships between different angles and apply this knowledge to more complex geometric concepts.
7th Grade Geometry Questions and Answers
Geometry is a branch of mathematics that deals with the properties and relationships of lines, angles, shapes, and space. It is an important subject for 7th graders to study, as it lays the foundation for more advanced mathematical concepts. Here are some common geometry questions and their answers that are often covered in the 7th grade curriculum:
1. What is the difference between a line, line segment, and ray?
Line: A line extends indefinitely in both directions. It has no endpoints.
Line segment: A line segment is a part of a line that has two endpoints.
Ray: A ray is a part of a line that has one endpoint and extends infinitely in one direction.
2. How do you measure the area and perimeter of a rectangle?
To measure the area of a rectangle, you multiply its length by its width. The formula for the area of a rectangle is A = length × width.
To measure the perimeter of a rectangle, you add all four sides together. The formula for the perimeter of a rectangle is P = 2(length + width).
3. What are the types of angles?
Acute angle: An angle that measures less than 90 degrees.
Right angle: An angle that measures exactly 90 degrees.
Obtuse angle: An angle that measures more than 90 degrees but less than 180 degrees.
Straight angle: An angle that measures exactly 180 degrees.
Reflex angle: An angle that measures more than 180 degrees but less than 360 degrees.
4. How do you find the volume of a rectangular prism?
To find the volume of a rectangular prism, you multiply its length, width, and height. The formula for the volume of a rectangular prism is V = length × width × height.
5. What is the Pythagorean Theorem?
The Pythagorean Theorem states that in a right triangle, the square of the length of the hypotenuse (the side opposite the right angle) is equal to the sum of the squares of the lengths of the other two sides. The Pythagorean Theorem is often written as a^2 + b^2 = c^2, where a and b are the lengths of the legs of the right triangle, and c is the length of the hypotenuse.
These are just a few examples of the types of geometry questions and answers that 7th graders may encounter. By understanding these concepts and practicing with various problems, students can develop a strong foundation in geometry.
What is Geometry?
Geometry is a branch of mathematics that deals with the study of shape, size, and properties of figures and spaces. It explores the relationship between points, lines, angles, surfaces, and solids. Geometry plays a crucial role in various fields such as architecture, engineering, art, and physics.
One of the fundamental concepts in geometry is the notion of a point. A point is a precise location in space that has no size or dimension. Points are represented by a dot and are used as building blocks for constructing figures.
Another important concept in geometry is a line. A line is a straight path that extends infinitely in both directions. It has no thickness and is composed of an infinite number of points. Lines are used to connect points and create shapes.
Geometry also deals with angles, which are formed by two rays that share a common endpoint called a vertex. Angles are used to measure the amount of rotation or separation between two lines or surfaces. They can be classified as acute (less than 90 degrees), right (exactly 90 degrees), obtuse (between 90 and 180 degrees), or straight (exactly 180 degrees).
In addition to points, lines, and angles, geometry studies different types of shapes such as triangles, quadrilaterals, circles, and polygons. Triangles are three-sided polygons, quadrilaterals have four sides, and polygons have multiple sides. Circles are a set of points equidistant from a fixed point called the center. These shapes have specific properties and formulas that enable mathematicians to calculate their sizes, areas, and angles.
Geometry serves as a foundation for understanding the physical world around us. It helps us comprehend the properties of shapes and their relationships, enabling us to solve real-world problems. Whether it’s designing buildings, creating computer graphics, or analyzing the movement of celestial bodies, geometry is an essential tool for exploring and understanding our environment in a structured and logical manner.
Types of Geometric Shapes
In geometry, there are various types of geometric shapes that are classified based on their characteristics and properties. These shapes can be two-dimensional or three-dimensional, and they play a significant role in understanding the principles and concepts of geometry.
1. Triangles: Triangles are polygons with three sides. They can be classified based on the length of their sides or the size of their angles. Some common types of triangles include equilateral triangles, isosceles triangles, and scalene triangles.
2. Quadrilaterals: Quadrilaterals are polygons with four sides. They can have different combinations of angles and side lengths. Some common types of quadrilaterals include squares, rectangles, parallelograms, and trapezoids.
3. Circles: Circles are perfectly round shapes that have a set of points that are equidistant from a central point called the center. They are defined by their radius (the distance from the center to any point on the circle) and diameter (twice the radius).
4. Polygons: Polygons are closed figures with straight sides. They can have any number of sides and angles. Some common types of polygons include pentagons, hexagons, and octagons.
5. Solids: Solids are three-dimensional shapes that have length, width, and height. They can be classified based on the number of faces, edges, and vertices they have. Some common types of solids include cubes, spheres, cylinders, and pyramids.
Understanding the different types of geometric shapes is essential in learning and solving problems in geometry. By recognizing and identifying these shapes, one can analyze their properties and relationships to solve various mathematical problems.
Understanding Angles
An angle is a geometric figure formed by two rays emanating from a common endpoint, called the vertex. It can be measured in degrees, radians, or a fraction of a circle.
Angles can be classified based on their measures:
- Acute angles: these angles have measures between 0 and 90 degrees.
- Right angles: they have a measure of exactly 90 degrees.
- Obtuse angles: these angles have measures between 90 and 180 degrees.
- Straight angles: they have a measure of exactly 180 degrees.
- Reflex angles: these angles have measures between 180 and 360 degrees.
When two angles add up to 90 degrees, they are called complementary angles. For example, if one angle measures 30 degrees, its complementary angle would measure 60 degrees.
On the other hand, when two angles add up to 180 degrees, they are called supplementary angles. For instance, if one angle measures 120 degrees, its supplementary angle would measure 60 degrees.
Understanding the properties and classifications of angles is crucial in geometry as it allows us to solve problems involving shapes, lines, and measurements. It helps us analyze and describe the relationships between different parts of a figure or system.
Properties of Triangles
A triangle is a polygon with three sides and three angles. It is one of the basic shapes studied in geometry. Triangles have several properties that help us understand and classify them.
1. Types of Triangles: Triangles can be classified based on the lengths of their sides and the measures of their angles. There are three main types of triangles: equilateral, isosceles, and scalene. An equilateral triangle has three equal sides and three equal angles. An isosceles triangle has two equal sides and two equal angles. A scalene triangle has no equal sides or angles.
- Example: Triangle ABC has all its sides equal, so it is an equilateral triangle.
- Example: Triangle XYZ has two sides of equal length, so it is an isosceles triangle.
- Example: Triangle PQR has no sides or angles that are equal, so it is a scalene triangle.
2. Angle Measures: The sum of the interior angles of a triangle is always 180 degrees. Each angle in a triangle can be classified as acute, obtuse, or right. An acute angle is less than 90 degrees, an obtuse angle is greater than 90 degrees, and a right angle is exactly 90 degrees.
- Example: Triangle ABC has angle A measuring 60 degrees, angle B measuring 70 degrees, and angle C measuring 50 degrees. The sum of these angles is 180 degrees.
- Example: Triangle XYZ has angle X measuring 100 degrees, angle Y measuring 40 degrees, and angle Z measuring 40 degrees. The sum of these angles is also 180 degrees.
- Example: Triangle PQR has angle P measuring 90 degrees, angle Q measuring 45 degrees, and angle R measuring 45 degrees. The sum of these angles is again 180 degrees.
3. Triangle Inequality Theorem: The sum of the lengths of any two sides of a triangle must be greater than the length of the third side. This theorem helps us determine if a given set of side lengths can form a triangle.
- Example: If side AB measures 5, side BC measures 7, and side AC measures 10, we can check if these lengths satisfy the triangle inequality theorem: 5 + 7 > 10, 5 + 10 > 7, and 7 + 10 > 5. Since all three inequalities are true, these lengths can form a triangle.
- Example: If side XYZ measures 4, side YZ measures 7, and side XZ measures 15, we can check if these lengths satisfy the triangle inequality theorem: 4 + 7 > 15, 4 + 15 > 7, and 7 + 15 > 4. Since the first inequality is false, these lengths cannot form a triangle.
Calculating Perimeter and Area
When studying geometry, one important concept to understand is how to calculate the perimeter and area of shapes. These measurements allow us to quantify the size and dimensions of different objects.
Perimeter
The perimeter of a shape is the total distance around its outer edges. It can be calculated by adding up the lengths of all the sides. For example, when dealing with a rectangle, you would add the lengths of all four sides together to find the perimeter.
It is important to note that the units used for measuring the sides must be the same in order to calculate an accurate perimeter. For example, if the length of one side is given in meters, then all the other sides should also be measured in meters. This consistency ensures that the final answer represents a meaningful measurement of the total distance around the shape.
Area
The area of a shape is the total amount of space it occupies. It can be calculated differently depending on the shape in question. For rectangles and squares, the area is found by multiplying the length and width together.
Other shapes, such as triangles and circles, have their own formulas for calculating area. For a triangle, the area can be found by multiplying the base by the height and dividing the result by 2. For a circle, the area can be found by multiplying the square of the radius by pi (approximately 3.14159).
Understanding how to calculate perimeter and area is essential in geometry as it allows us to solve real-life problems involving measurements, such as determining the amount of fencing needed for a plot of land or the area of a room for carpeting. These calculations help us apply mathematical concepts to the world around us.
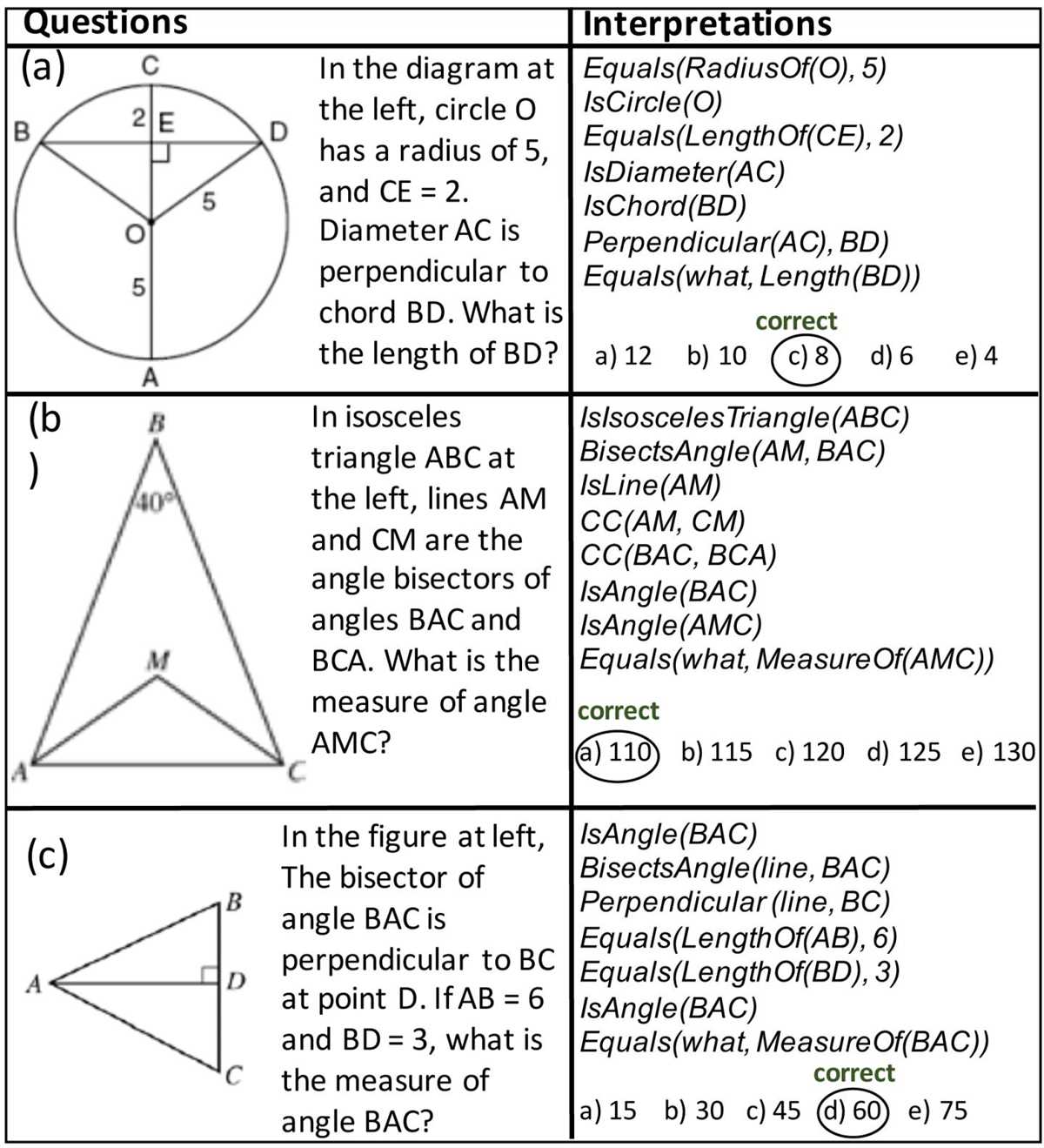
Similarity and Congruence of Figures
Understanding the concepts of similarity and congruence of figures is crucial in the field of geometry. These concepts allow us to analyze and compare different geometric shapes based on their attributes and properties.
Similar figures are shapes that have the same shape but may differ in size. In other words, they have proportional sides and angles. To determine if two figures are similar, we can use the ratio of their corresponding side lengths or the equality of their corresponding angle measures. Similar figures can be transformed through dilation, where the shape is enlarged or reduced while maintaining its proportions.
Congruent figures, on the other hand, are shapes that have exactly the same size and shape. They have equal side lengths and equal angle measures. Congruence can be established through the application of rigid transformations, such as translations, rotations, and reflections. These transformations preserve the shape and size of the figures.
Understanding the similarity and congruence of figures allows us to solve various geometric problems, such as finding missing side lengths and angle measures, determining the scale factor between similar figures, and proving the congruence of triangles. These concepts are important in real-life applications, such as architecture, engineering, and map scaling.